Compression Molding

Process Overview: Compression Molding
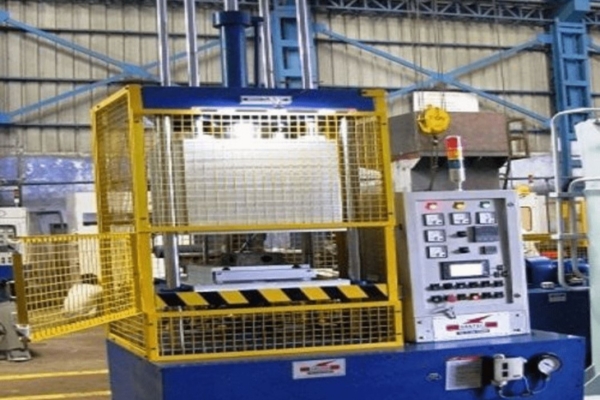
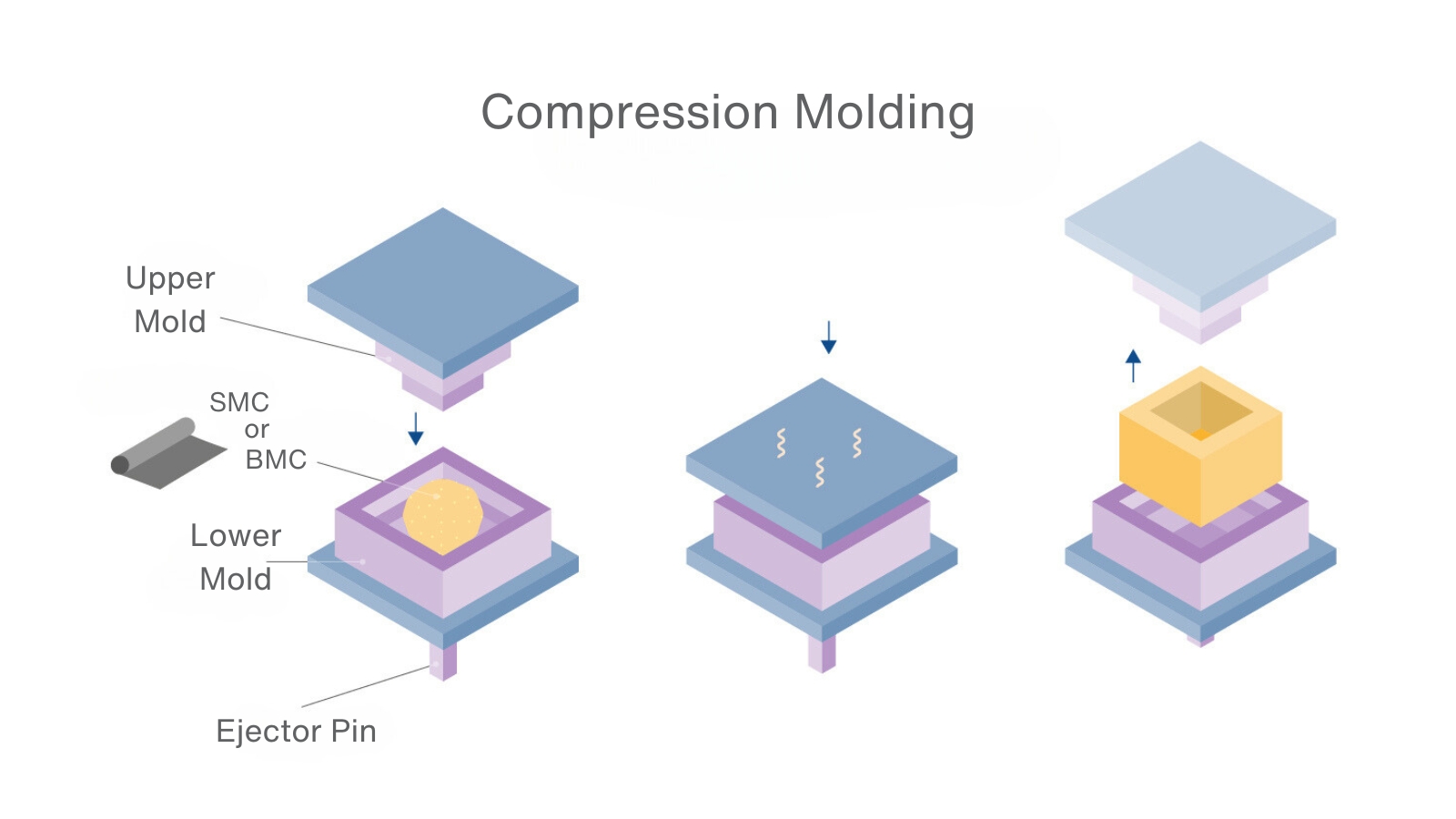
Compression molding includes several specific processes using a hydraulic press or autoclave to apply heat and pressure to a material charge in a metal mold or mold set, where the part is formed, consolidated, and cured. Compression molded parts include flat sheets, deep draw profiles, or complex or intricate parts with detailed features.
Several types of consolidated composite materials are used in compression molding including Sheet Molding Compound (SMC), Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) and prepreg. Other options include Thick Molding Compound (TMC) and wet molding. Reinforced thermoplastics can also be used with this process in forms such as organosheets, slit‐tape fabrics, and commingled fabrics.
Sheet Molding Compound (SMC)
SMC is a thickened polyester/vinyl ester/epoxy resin combined with chopped glass or carbon fibers formed on a SMC machine into a pliable sheet of material. The SMC sheet is rolled and allowed to mature to allow the thickening process to occur and increase viscosity. When ready, a pre‐weighed charge of SMC is inserted in the mold cavity which is closed under pressure to form and cure the part.
Bulk Molding Compound (BMC)
BMC is a highly viscous material created by mixing polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy resin with chopped glass or carbon fibers and fillers. It is inserted into the mold cavity as a dough ball rather than a sheet. BMC requires no thickening time and can be used immediately.
Technical and HSE Support for Compression Molding
Composites One offers personalized technical support for customers manufacturing with the process of compression molding, as well as the most up-to-date information on regulatory and compliance requirements.

